Table of Contents Show
Understanding partition schemes is essential for efficient organization and utilization of hard drives in computer storage. MBR (Master Boot Record) and GPT (GUID Partition Table) are two prominent schemes that offer distinct advantages and limitations. In this guide, we explore the intricacies of MBR and GPT, including their features, differences, and suitability for various computing needs.
We explain the fundamental concepts, provide step-by-step instructions on checking partition styles, and offer guidance on converting between MBR and GPT without data loss. Whether you’re a novice user seeking clarity or an experienced tech enthusiast looking to optimize storage strategies, this guide equips you with essential knowledge for effective disk management. So, if you want valuable insights into navigating the world of partitioning schemes, this guide is for you.
What is a Partition?
A partition is like dividing a big cake into smaller slices. Imagine your computer’s hard drive as that cake. Instead of treating it as one big chunk, we split it into separate sections. Each section acts like its own mini hard drive.
These sections are managed by your computer’s operating system, like Windows or macOS. They keep things organized, so it’s easier to find and manage files.
When you turn on your computer, a special part of the hard drive called the boot sector kicks things off. It tells your computer where to find the operating system so it can start up properly.
Think of partitions as different rooms in a house. Each room has its own purpose, like a kitchen for cooking or a bedroom for sleeping. Similarly, partitions have different functions, like storing programs or keeping your personal files.
And just like how you can only sleep in one bed at a time, your computer can only boot from one partition at a time. That’s why we have something called the “active” partition, which holds the operating system and gets things going when you start up your computer.
So, partitions are like organized sections on your hard drive that help your computer run smoothly and keep your files in order.
What is an MBR partition?
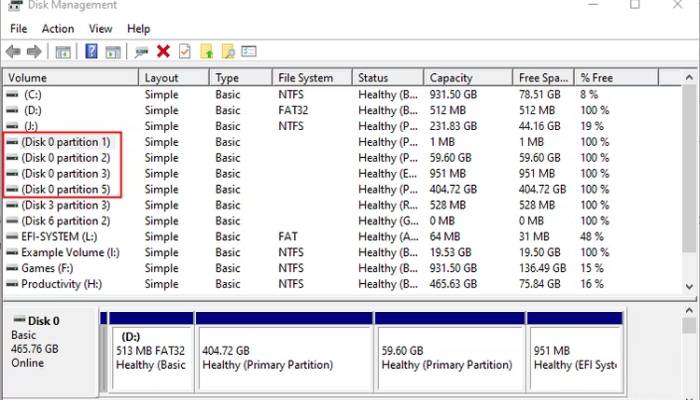
MBR, or Master Boot Record, is an older disk format introduced in 1983. It’s called MBR because of a special sector at the start of the disk, acting like a master guide for the whole disk. This layout divides the disk into primary and extended partitions.
Primary partitions are where you install your operating system, making them crucial for booting up your computer. You can have up to four primary partitions on an MBR disk.
Extended partitions are like containers. They hold logical drives, which are smaller partitions used for organizing files. But extended partitions themselves don’t have drive letters or file systems.
Here’s the catch: an MBR disk can only handle up to 2TB of space. If you have a larger disk and stick with MBR, you’re limited to just 2TB of usable space. To make more partitions beyond the four-primary limit, you need to convert one primary partition into an extended one.
Despite its age, MBR is still widely used because it’s compatible with older systems and simpler setups. But if you need more space or want faster boot times, you might want to consider using GPT instead.
Advantages and Disadvantages Of MBR
Advantages
- Compatibility: MBR works well with older systems, operating systems, and disk utilities, making it suitable for legacy BIOS firmware.
- Familiarity: MBR has been the standard for a long time, so many users and administrators are familiar with its setup and management processes.
- Simplicity: MBR is simple and lightweight, occupying minimal space on the disk and having a straightforward structure, which makes it easy to manipulate and repair.
Disadvantages
- Limited partition size: MBR restricts partition size to 2 terabytes, which can be insufficient for larger storage needs.
- Partition limitations: MBR allows a maximum of four primary partitions or three primary partitions and one extended partition, which may not be adequate for complex setups requiring multiple partitions.
- Lack of data redundancy: MBR does not include built-in mechanisms for data redundancy or integrity checks, making it susceptible to data loss or booting issues if the MBR or partition table gets corrupted.
What is GPT Partition?
GPT, or GUID Partition Table, is the latest method for organizing partitions on a hard disk. It’s considered superior to MBR due to its flexibility and compatibility with modern hardware.
Unlike MBR, which has limitations on partition size and quantity, GPT can handle theoretically unlimited partitions, though most operating systems cap it at 128. Each partition in GPT can hold up to a staggering 9.44 zettabytes (1 zettabyte equals 1 billion terabytes) of data, making it ideal for large storage needs.
One of the main features of GPT is its use of Globally Unique Identifiers (GUIDs) to define partitions. This ensures that each partition has a unique identifier, enhancing reliability and preventing conflicts.
GPT also includes a primary GPT header at the start of the disk and a secondary GPT header at the end. This redundancy helps in case of corruption, as the backup headers and partition tables can be used for recovery.
Additionally, GPT disks have a protective MBR at the first sector, which prevents older disk utilities from misidentifying or damaging the disk.
Overall, GPT offers better data integrity, flexibility, and support for larger drives compared to the older MBR partitioning scheme.
Advantages and Disadvantages of GPT
Advantages
- Large partition size: GPT supports significantly larger partition sizes, up to 9.4 zettabytes, making it suitable for high-capacity storage needs.
- Increased partition numbers: GPT supports up to 128 primary partitions, providing flexibility for multi-boot systems and scenarios requiring multiple partitions.
- Data redundancy and integrity: GPT includes redundant copies of critical data structures and CRC32 checksums to verify data integrity, enhancing data protection and recovery capabilities.
Disadvantages
- Compatibility with legacy systems: GPT requires UEFI firmware for full utilization, limiting compatibility with older systems using legacy BIOS.
- Operating system and software support: While most modern operating systems support GPT, older versions may have limitations or lack support.
- Learning curve: GPT introduces a new partitioning scheme that may require users to familiarize themselves with new setup and management procedures, posing a minor inconvenience for those accustomed to MBR.
How to Check If Your Drive Uses MBR or GPT
To determine whether your current drive is using MBR or GPT partition style, you can follow these simple steps:
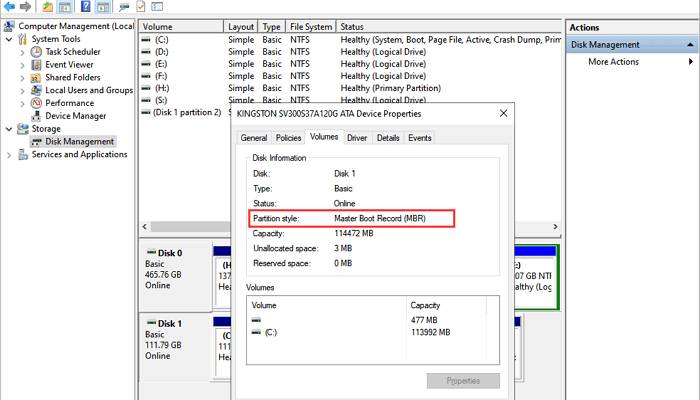
Step 1: Open Disk Management – You can do this by right-clicking on “This PC” and selecting “Manage”. After that, navigate to “Disk Management”.
Step 2: Examine Disk Properties – Right-click on the drive that you want to check and choose “Properties”.
Step 3: Check Partition Style – In the “Volumes” tab of the properties window, locate the partition style listed under the disk information. It will specify whether the drive uses MBR or GPT partition style.
Differences between MBR and GPT Partition
The table presented below illustrates the main distinctions between MBR and GPT Partition.
| Point of Comparison | MBR- Master Boot Record | GPT- GUID Partition Table |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Primary Partitions | 4 | Up to 128 for Windows OS. |
| Maximum Partition size | 2 TB | 18 exabytes (18 billion gigabytes) |
| Maximum hard drive size | 2 TB | 18 exabytes (18 billion gigabytes) |
| Security | No check sum on data sector | CRC values are used to ensure data security. Back up GUID partition table. |
| Specifications | BIOS | UEFI |
| Partition Name | Is stored in the partition | Has a unique GUID and a 36 character name |
| Multiple boot supported | Poor support | Boot loader entries are in different partitions |
| Operating System Support | Windows 7 and other older versions like Windows 95/98, Windows XP etc. | All major OS like MAC and latest versions of Windows like Windows 10. |
| Data recovery | Data cannot be recovered easily. | Data can be easily recovered. |
| Data Corruption | No way to detect corruption of data. | Easy to detect |
| Method of Partition Addressing | CHS (Cylinder Head Cycle) or LBS (Logical Block Addressing) | LBA is the only method of addressing partitions. |
| Size | 512 bytes | 512 bytes per LBA. Each partition entry is 128 bytes. |
| Partition type code | 1 byte code | 16 byte GUID is used. |
| Stability | Less stable as compared to GPT | Offers more security. |
| Bootable Version of OS | Boots 32 bit operating system | Boots 64 bit operating system |
| Storage | Only upto 2TB capacity. Disk size >2TB is marked as unallocated and cannot be used. | Disk capacity of 9.44 million TB |
| Performance | Lower in performance compared to GPT. | Offers superior performance if UEFI boot is supported. |
How to Convert MBR to GPT (or GPT to MBR) Without Losing Data
Converting your hard drive or SSD between the MBR and GPT partition styles can be tricky, but it doesn’t have to result in deleting all your data. The key is to use the right conversion tool to minimize the risk.
While there are various utilities that can convert partitions, the one that we recommend is EaseUS Partition Master. Here’s why it’s the best for safe conversions:
– It’s completely free to use for MBR to GPT or vice versa conversions.
– The process is simple and automated, with no need for complex command line options.
– It allows conversion without deleting or destroying any of your stored data.
– It has a simple interface that anyone can understand.
– It provides a full backup of partitions before making any changes.
– It allows resizing of partitions to properly align with GPT requirements.
– It includes different other useful features for free.
By using EaseUS Partition Master, you can safely change between MBR and GPT styles without worrying about lost files, applications, or other important data. It’s the simplest, most reliable method.
To use EaseUS Partition Master for safe MBR to GPT conversion, you need to:
1. Download and install EaseUS Partition Master.
2. Launch EaseUS Partition Master once installed.
3. Locate and press the “Disk Converter” tab.
4. Select the partition that you want to convert.
5. Double-check that it is the correct disk, then click ‘Convert’ to convert.
The process is automated – EaseUS will handle the technical restructuring of the disk partitions behind the scenes. Your data remains intact.
NOTE: The same general steps can be followed to convert from GPT back to MBR as well.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the differences between MBR and GPT partitioning schemes is essential for effective disk management. While MBR offers compatibility with older systems and simplicity, GPT provides greater flexibility, support for larger capacities, and enhanced data integrity features.
When deciding between MBR and GPT, consider your specific needs and hardware compatibility. If you’re working with older systems or smaller disk capacities, MBR may suffice. However, for modern systems and larger storage requirements, GPT is the recommended choice due to its superior capabilities.
The process of converting between MBR and GPT partition styles can be accomplished safely and efficiently using tools like EaseUS Partition Master. By following the appropriate steps and precautions, you can ensure a smooth transition without risking data loss or system instability.
In summary, while MBR has been a longstanding standard, GPT represents the future of disk partitioning, offering unparalleled flexibility and reliability. By embracing GPT, users can harness the full potential of their storage devices while ensuring compatibility with modern hardware and operating systems.
FAQ
Q: What is MBR?
A: MBR stands for Master Boot Record, which is a partitioning scheme used to define the layout of a storage device.
Q: What is GPT?
A: GPT stands for GUID Partition Table, a modern partitioning scheme used for defining the partition layout of a storage device.
Q: What is the main difference between MBR and GPT?
A: The main difference lies in the maximum disk size they support, with MBR supporting up to 2 TB and GPT supporting disks of any size.
Q: How many partitions can MBR support?
A: MBR can support up to four primary partitions or three primary partitions and one extended partition.
Q: How many partitions can GPT support?
A: GPT can support up to 128 partitions, providing more flexibility for partitioning needs.
Q: Which operating systems support MBR?
A: MBR is supported by most operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and macOS.
Q: Which operating systems support GPT?
A: GPT is supported by most modern operating systems, including Windows 10, macOS, and many Linux distributions.
Q: Can MBR disks be converted to GPT?
A: Yes, MBR disks can be converted to GPT, but the process requires wiping the disk, so it’s important to back up any important data before proceeding.
Q: Can GPT disks be converted to MBR?
A: Yes, GPT disks can be converted to MBR, but like the previous question, the process requires wiping the disk, so data backup is crucial.
Q: Can MBR and GPT coexist on the same disk?
A: No, MBR and GPT cannot coexist on the same disk. A disk must use either MBR or GPT as its partition scheme.